
The OCIMF document on anchoring refers to MEG Edition 3 however, MEG has been updated to Edition 4, and the same shall be referred to in this article. The environmental loads of wind and current are estimated from the non-dimensional coefficient curves provided in the OCIMF document, which in turn are taken from OCIMF Mooring Equipment Guidelines (MEG). Step 1: Calculating the environmental loads the catenary effect of the anchor chain is not considered.
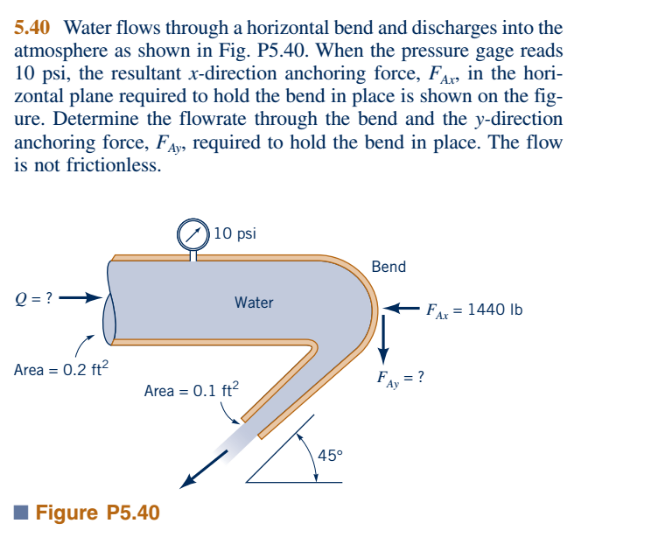
wave drift forces have been estimated using a Pierson-Moskowitz sea spectrum.As a result, only the longitudinal components of the wind, waves and current forces need be considered. the vessel lies at anchor such that the lead of the anchor chain is parallel to the centreline of the vessel.the anchored vessel is in a steady position, having swung at anchor in the direction of the dominant environmental force or has reached an equilibrium position.the vessel is lying to a single anchor.Interaction effects between the forces are not considered.
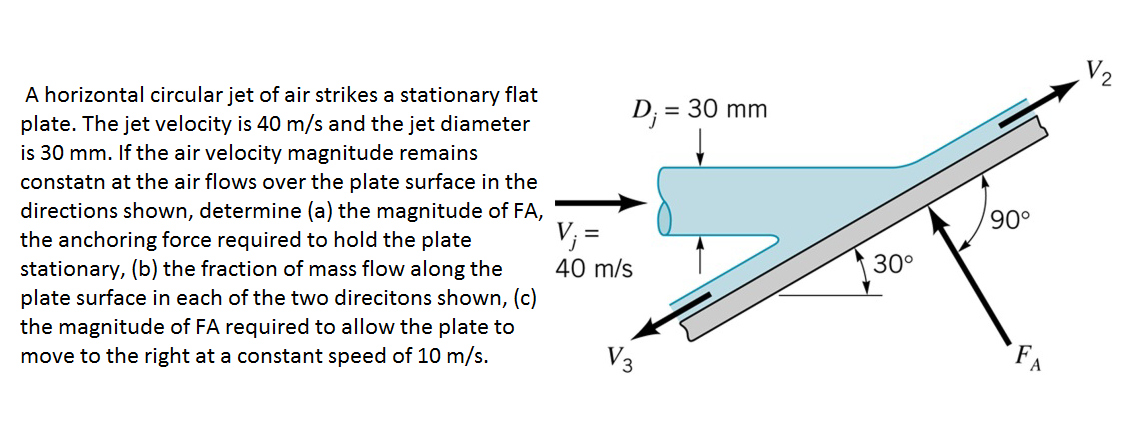
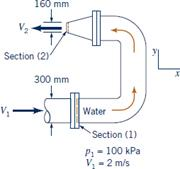
The method is based on OCIMF’s publication ‘ Estimating The Environmental Loads On Anchoring Systems‘. In this article we will present a simple method based to estimate the holding power required for an anchor operating in a given environmental condition. While vessel masters have reliable experience in knowing the holding power of their vessels and decide based on their invaluable practical knowledge, an estimate of the forces which the vessel is experiencing in a particular weather is always useful in knowing whether the anchor can hold or not, helping in critical decision making on whether to remain at anchor or let go – thus saving the vessel from a potential damage of anchoring systems. Thus, it is critical to know if the anchor has enough holding power when the weather goes inclement. The anchor is supposed to hold the vessel in varying environmental conditions depending on where the vessel is being anchored. When a vessel is at anchor, it swings to align itself along the direction of the dominant environment. Anchoring is a fundamental and sensitive operation for a vessel.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
